Understanding AQI and Our Environment
- Science Holic
- Aug 6, 2025
- 3 min read
Author: Rui Zhang
Editors: Sophia Chen, Hwi-On Lee, Jaylen Peng
Artist: Emily Tai
Nowadays, many families have indoor air quality monitors that display air quality measures such as AQI, PM2.5, and PM10 levels. These measurements are important since they can provide us with a broad understanding of pollution and the quality of the air in our communities. By acknowledging these issues, people can take action to prevent exposure to polluted air and protect our environment more effectively. However, most people often ignore these measurements due to a lack of understanding of what they indicate.
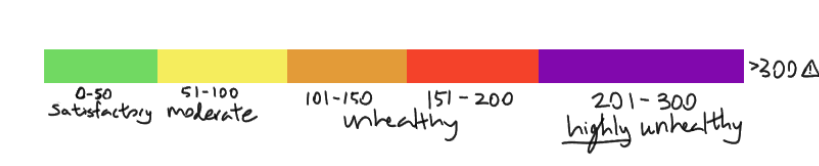
The AQI (Air Quality Index) ranges from 0 to 500, with higher numbers indicating increased pollution, such as ground-level ozone, particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and greater health risks. To help the average person understand the values of the AQI, scientists chose to divide the scale into six color-coded categories that show the level of concern regarding the air quality. Green (0-50) means that the air is satisfactory and poses no risk of air pollution. Yellow (51–100) indicates the air is moderate, which is the most common measurement found in urban cities. This category may pose a slight concern for those with lung issues and certain populations who are sensitive to bad air quality. Orange (101–150) and red (151–200) show that air pollution has reached levels that can affect people’s health, mainly those with respiratory conditions. Purple (201–300) typically occurs when there is a wildfire in the area, indicating an air quality that is highly unhealthy. Maroon, representing an AQI of over 300, signifies hazardous air quality and poses serious health risks to the entire environment around it.

AQI tracks five major pollutants: ground-level ozone, particle pollution (PM2.5 and PM10), carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide. All these pollutants are known to have negative health effects. While all five are important, most people tend to focus on the AQI and PM levels, since these are the only two measurements that appear on indoor monitors. These measurements can be especially beneficial during wildfires, as they can serve as a pre-warning system. For example, in the recent Eaton Fire in the LA area, many residents relied on AQI measurements as a significant factor to decide whether to take protective measures such as wearing masks or limiting outdoor activities. These measurements also help individuals understand when to use air purifiers to improve air quality within the house. Mountain-based scientific monitoring stations in Arcadia, Altadena, and Pasadena utilize professional equipment to measure AQI, enabling scientists to better understand wildfire behavior. Therefore, it's a promising tool for future wildfire prevention. People are training AI models to read AQI and PM measurements now to forecast fire risk in certain areas. If developed well, this could be a game-changer in reducing wildfire damage and protecting communities.

“Just like we need to ingest water, we need to breathe air”, says Pistone from NASA. This quote reminds people how vital clean air is for human health. Even short-term exposure to polluted air can cause coughing, throat irritation, and shortness of breath. Long-term exposure is linked to serious respiratory and cardiovascular issues, including chronic bronchitis, COPD, lung cancer, increased risk of heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure. Many of these conditions are irreversible and are primarily caused by PM2.5—a small particle in the air that people breathe in with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less. That’s why the AQI is so important. It provides a clear warning when the air is unsafe, enabling us to take action in challenging situations to avoid breathing in dangerous pollutants. Just as we’ve come to expect clean drinking water because we know it’s essential to our survival, we should hold the same expectation for the air we breathe every day.
Clean water is also essential for health and survival, but only about 3 percent of the water on Earth is freshwater, and a significant portion of that is locked up in glaciers and polar ice caps. Clean water has remained a huge pressing issue for current society, and high AQI levels can exacerbate the situation since air pollutants can lead to acidification and eutrophication of water bodies. Ultimately, it will damage the ecosystems and make the water unsafe for both humans and animals to drink. These changes also harm plants that rely on clean water to grow, which disrupts entire food chains and contributes to biodiversity loss.
Citations:
Loiacono, M. (2024, October 18). What is Air Quality? - NASA. NASA.
Home Page | AirNow.gov. (n.d.). Retrieved from AirNow website: https://www.airnow.gov/?
Los Angeles Air Quality Index (AQI) and California Air Pollution | AirVisual. (n.d.). Retrieved
from IQAir website: https://www.iqair.com/us/usa/california/los-angeles



Comments